When talking about keeping cryptocurrencies safe, wallets often slide under the radar. Yet finding a secure wallet is one of the most important tasks for any crypto trader or investor.
That’s why we’ve written this review of the different types of cryptocurrency wallets and how to best use them. We also discuss some issues that have emerged in recent years, and how to avoid those problems.
The purpose of cryptocurrency wallets
This part is quite straightforward. Cryptocurrency wallets are online storage units where you can keep your digital coins and transfer them in and out at your leisure. Each wallet has a unique address code that allows users to send and receive coins anytime, anywhere.

Those are the basics, but there are several other factors to take into account when choosing cryptocurrency wallets. These include transaction fees and speed settings, ledger records, and types of crypto storage. Let’s take a closer look at the options.
Transactions and ledger records
A public ledger record notes each transaction that takes place in a particular blockchain network. In most networks, these records hold all the important information that comprises a transaction. This includes address codes (sender & receiver), the number of coins transferred, and the time of the transfer. Anyone can view these transactions. As such, these ledgers record and show everything you do with a wallet.
Each wallet generates address codes. Some use a single static code, while others generate a new address for each transaction. The second option is more secure.
You should also be aware of the transaction system, speed, and costs before choosing a wallet. Some coins (such as BTC) require confirmations from third parties to allow your transfer take place. Other blockchains use a scripted online contract (an Ethereum smart contract), which sets agreed-upon requirements that you need to meet for the transaction to take place.
In the first case, you pay a small fee to miners to keep the transfer system running. However, with huge numbers of transactions per second, this system can be slow. Using smart contracts allows for lower costs and much faster deposits/withdrawals.

Hot vs cold storage
Many wallets exist only when connected to the internet. These are known as hot wallets. They include online platforms where you sign in with your account and public keys are provided for you.
Cold storage wallets can also operate offline, albeit with limited services. You still need an internet connection to send or receive coins, but you can but check your balance while you’re offline. Cold wallets include desktop, paper, and hardware wallets.
“Hot” cryptocurrency wallets
Hot wallets are the most common crypto storage platforms, but they’re also known for their weak security measures. Many of these are free services that use public keys. These online wallets are appropriate for quick transactions, such as trading or exchanging small quantities of coins. They also come in handy for beginners who want to learn about the crypto world without making any big investments.

Famous hot wallets include Blockchain.com, BTC.com, MyEthereWallet, MetaMask, LiteVault, Gatehub, Astral, NanoWallet, and GUI LightWallet.
Desktop wallets
Desktop wallets are the original form of coin storage; they’ve been around since the industry began in 2009. In many ways, these are superior to their online counterparts. With desktop wallets, you can download the software and keep your keys private. They also allow you to generate recovery seed codes, which block the program if you suspect your wallet was compromised. However, if your computer falls victim to viruses or technical programs, you lose your crypto as well.

Famous desktop wallets include Electrum, Jaxx, Exodus, Armory, GreenAddress, Copay, Ethereum Wallet, Daedalus, Litecoin Core Wallet, Rippex, and Verge Electrum. Downloading and using desktop cold storage software is free these days.
Mobile wallet apps
As the crypto market matures, more and more clients have begun to demand mobile cryptocurrency wallets. Now, both iOS and Android users can download and use mobile apps to store their crypto. These sit somewhere in between desktop and online platforms, blending easy-to-navigate interfaces with private keys. However, if you lose your phone or sell it without transferring your coins out, you can consider your balance lost.
Check out mobile apps like Uphold, Coinbase app, Coinomi, Bread Wallet, Mycelium, Edge, LoafWallet, and Cryptonator. Although a few of these charge for their services, most mobile wallet apps are free to use.
Paper cryptocurrency wallets
Paper wallets are handy to have, but a pain to set up on your own. Or, at least they were in the past. Nowadays, you can download your own QR codes and print them out on a piece of paper to use only when necessary. You can also connect these with any other platform, since you physically hold the single address code.

Of course, you must take care not to lose or damage your paper wallet. If you do, your balance is as good as gone, unless you’d already synchronized the paper wallet with an online platform. Paper wallets are usually free unless purchased from an exchange.
Hardware wallets
Hardware devices are the latest and most advanced crypto storage option. These HD wallets – which look and act like USB sticks – are the safest way to store your cryptocurrencies. The safety features of a hardware wallet include physical button confirmation of transfers, PIN and password codes, and a screen for offline balance inquiry. You can also sync your hardware wallet with other platforms if needed, provided the two are compatible.
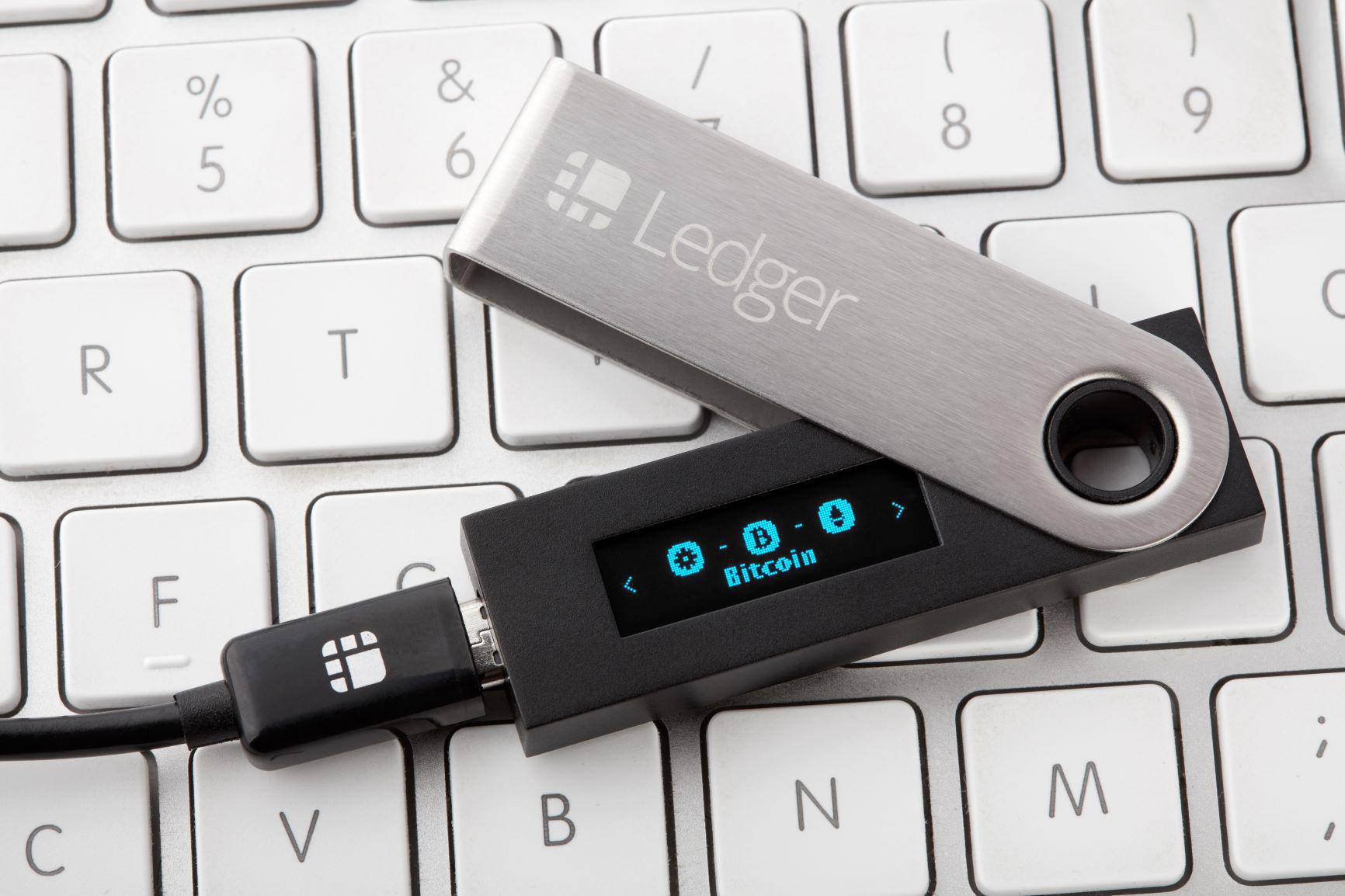

The biggest downside of hardware wallets is, of course, their price tag. However, for major investors, it’s a small price to pay for maximum security. The most famous models right now are Ledger Nano, TREZOR, KeepKey, and CoolWallet S.
Which of these wallets do you use? Let us know in the comments below.

